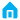
In the digital age, the need for high-speed, reliable communication has never been greater. At the
heart of this technological revolution lies optical fiber, a marvel of engineering that has transformed
how we transmit data. From internet access to telecommunications and beyond, optical fiber is the
backbone of modern communication systems. Here’s an in-depth look at the essential knowledge
surrounding optical fiber.

What is Optical Fiber?
Optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter
slightly thicker than that of a human hair. These fibers are used most often as a means to transmit
light between the two ends of the fiber, enabling high-speed data transfer over long distances with
minimal loss.

How Does Optical Fiber Work?
Optical fibers work based on the principle of total internal reflection. When light enters the fiber, it
bounces off the walls of the core and is guided through the fiber. The core is surrounded by a clad-
ding layer with a lower refractive index, which keeps the light within the core. This design ensures
that the light signals can travel long distances with minimal attenuation (signal loss).
Types of Optical Fibers
There are two main types of optical fibers, each with its own applications and advantages:
1. Single-Mode Fiber (SMF):
- Core Diameter: Small, typically around 8-10 micrometers.
- Light Transmission: Allows only one mode of light to propagate.
- Use Case: Long-distance communication, such as telecommunications and internet backbone
connections.
- Advantage: Higher bandwidth and lower attenuation, making it ideal for long-haul data transm-
ission.
2. Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF):
- Core Diameter: Larger, typically around 50-62.5 micrometers.
- Light Transmission: Allows multiple modes of light to propagate.
- Use Case: Short-distance communication, such as within buildings or on campuses.
- Advantage: Easier to couple light into the fiber, making it cheaper and simpler to use for short-
range applications.
Applications of Optical Fiber
Optical fiber technology is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Telecommunications: Optical fibers are the foundation of modern telecommunication networks,
enabling fast and reliable data transmission over vast distances.
- Internet: Fiber-optic internet connections provide high-speed internet access to homes and bus-
inesses, supporting the growing demand for streaming, online gaming, and cloud services.
- Medical: In the medical field, optical fibers are used in endoscopy, minimally invasive surgeries,
and various imaging techniques.
- Defense and Aerospace: Optical fibers are employed in secure communication lines and advanced
sensor systems.
- Industrial Automation: They are used in sensors and data transmission in harsh industrial enviro-
nments.

Advantages of Optical Fiber
Optical fiber offers several key advantages over traditional copper cables:
1. Higher Bandwidth: Optical fibers can carry significantly more data than copper cables.
2. Longer Distances: Optical signals can travel much longer distances without the need for signal
boosters.
3. Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)**: Unlike copper cables, optical fibers are not
affected by electromagnetic interference, ensuring more stable and reliable data transmission.
4. Security: It is more difficult to tap into optical fiber cables without being detected, making them
more secure for transmitting sensitive information.
5. Size and Weight: Optical fibers are thinner and lighter than copper cables, making them easier to
install and handle.
Future of Optical Fiber
The future of optical fiber looks bright as technology continues to advance. With the growing demand
for higher data rates and more reliable communication networks, optical fiber technology is set to play
a crucial role in the development of next-generation communication systems, including 5G networks,
smart cities, and beyond.
In conclusion, optical fiber is an indispensable component of modern communication infrastructure,
offering unparalleled speed, reliability, and efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, the importance
of optical fiber will only grow, further cementing its role as the backbone of our interconnected world.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!